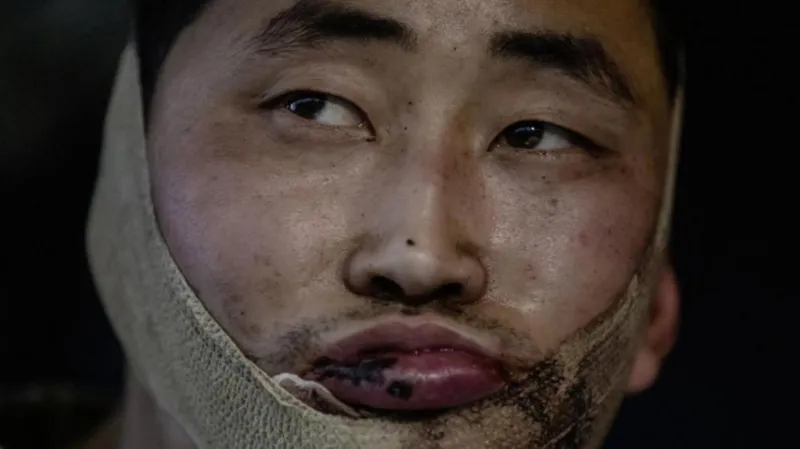
North Korean Troops Suffer Heavy Losses in Kursk: 40% Casualties in 3 Months
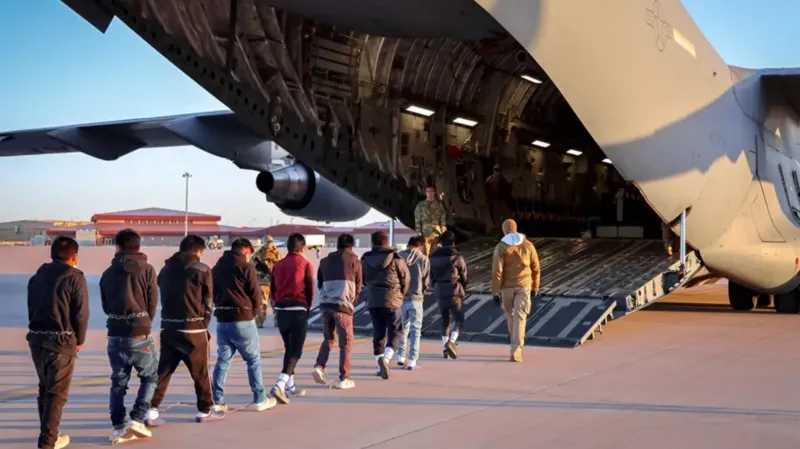
According to Western officials who spoke to the anonymity, North Korean forces have suffered devastating casualties in Russia’s western Kursk region during the past three months of fighting. An estimated 11,000 troops were deployed from the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) to aid Russian forces, but the toll has been staggering.
The officials reported that nearly 40% of the North Korean soldiers—around 4,000—have become battle casualties. This broad term encompasses those killed, wounded, missing, or captured in action. Of the 4,000 casualties, approximately 1,000 are believed to have been killed by mid-January alone.
The sheer scale of these losses has raised concerns within the DPRK, with officials acknowledging that such high casualty rates are unsustainable. The North Korean military, which is already under strain due to limited resources and the pressures of international sanctions, may struggle to replace the lost personnel, potentially affecting the country’s ability to continue its involvement in the conflict.
The rapid and severe losses signal a growing challenge for North Korean forces, and experts are questioning whether the country can maintain its presence on the battlefield in the long term. Given the severity of these casualties, North Korea might soon face tough decisions about whether to send reinforcements or reassess its involvement in the war.
As the conflict in Kursk rages on, the international community watches closely, with concerns about the sustainability of foreign military interventions and the long-term consequences for those involved.
The situation remains unclear regarding where the wounded are being treated and whether or when replacements will be sent to the front lines. However, the available data suggests that President Vladimir Putin’s ally, Kim Jong Un, is shouldering an extraordinarily high cost in supporting Russia’s efforts to expel Ukrainian forces from its territory. This move appears to be part of a strategy to strengthen Russia’s position ahead of potential ceasefire talks later this year.
In August, Ukraine launched a surprise offensive into the Russian oblast of Kursk, catching Russian border guards off guard. The attack was swift and effective, highlighting Ukraine’s tactical advantage. At the time, Kyiv made it clear that its goal was not to hold onto the territory seized but rather to use it as leverage in upcoming peace negotiations. This shift in tactics underscores Ukraine’s broader strategy of forcing Russia into a position where it would have to engage in serious talks, potentially altering the course of the conflict in the future.
As the conflict continues, the question of how and when the wounded will be treated, as well as the logistical challenges of maintaining a fighting force, remains critical. The consequences of these actions, both for the individuals involved and the broader geopolitical landscape, are still unfolding.
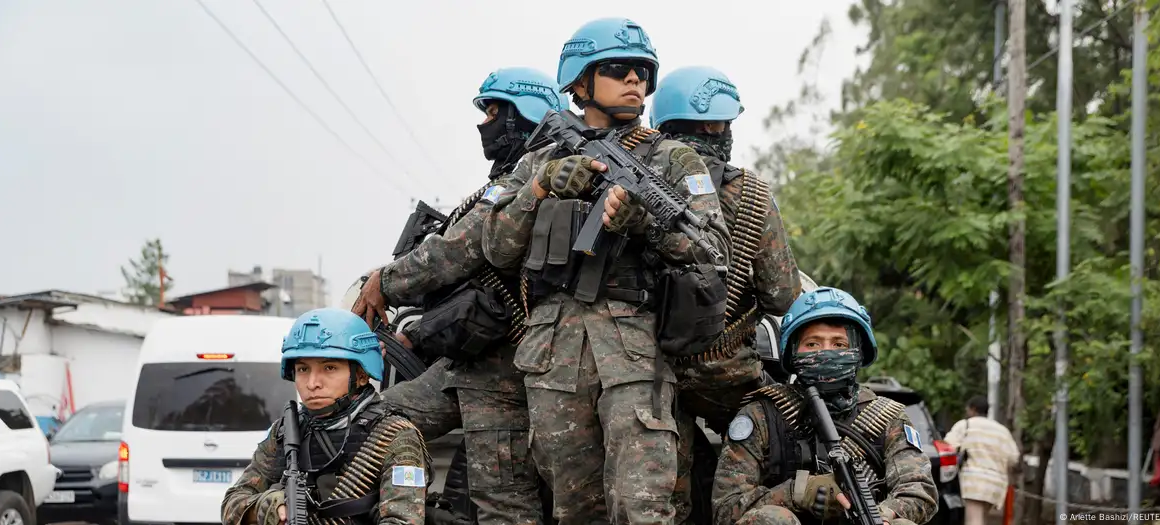
Since Ukraine’s initial success in Kursk, which saw swift territorial gains, the situation has shifted. Ukrainian forces have been steadily pushed back, a development that can be partially attributed to the arrival of North Korean troops in Russia in October. The deployment of these forces has significantly altered the balance of power on the front lines. Despite this, Ukraine still holds onto several hundred square kilometers of Russian territory and continues to inflict heavy losses on Russian forces.
The North Korean troops, reportedly from an elite unit known as the Storm Corps, have been thrust into the conflict with limited preparation and inadequate protection. Sources suggest that these troops have received minimal training, which raises concerns about their effectiveness in combat. In addition, reports indicate that they are being led by Russian officers, whose commands may be challenging for the North Koreans to follow due to language and cultural barriers.
Col. Hamish de Bretton-Gordon, a former British Army tank commander, highlighted the disparity in the training and leadership of these troops. “These are barely trained troops led by Russian officers whom they don’t understand,” he noted, emphasizing the challenges this presents for both the North Koreans and their Russian commanders. The lack of proper training and communication difficulties could prove to be a significant hindrance to the effectiveness of these forces in the ongoing conflict.
The situation on the front lines in Ukraine continues to evolve as the inclusion of North Korean troops has added a new dimension to the conflict. Reports from South Korean intelligence highlight the precarious position of these soldiers, who, according to some experts, are ill-prepared for the complexities of modern warfare. The North Koreans are being deployed in high-risk combat zones with limited training and resources, making them highly vulnerable.
According to military analysts, the North Korean soldiers are seen as “cannon fodder” by the Russian military, with little regard for their safety or wellbeing. The soldiers are reportedly being thrown into battle with minimal protection and without adequate understanding of modern combat tactics, particularly in dealing with sophisticated technologies like drones.
The use of First-Person-View (FPV) drones by the Ukrainian forces has become an increasingly effective tool in the conflict, especially in the southern regions of Ukraine, such as the Donbas area. These drones, which provide real-time video feeds to operators, allow Ukrainian forces to precisely target enemy positions with incredible accuracy. The drones have proven to be particularly effective against units that lack modern defensive technology, making the North Korean troops especially vulnerable to such attacks. The drones can target infantry from a distance, making it difficult for unprepared forces to respond.
Despite the dire circumstances, Gen Oleksandr Syrskyi, Ukraine’s top military commander, has warned that the presence of North Korean soldiers presents a significant challenge. While they may be poorly equipped and ill-prepared, their involvement in the conflict complicates Ukrainian efforts to push back Russian forces. North Korean soldiers could potentially overwhelm certain sectors of the front line, and the increasing number of these troops may pose strategic difficulties for Ukrainian forces already stretched thin by the ongoing conflict.
This situation underscores the growing complexity of the war as new alliances and military tactics shape the battlefield. The presence of foreign soldiers from North Korea, coupled with the continued use of drones and other modern technologies, makes for a volatile and unpredictable situation in the ongoing conflict between Ukraine and Russia.
The general described a significant force of approximately 11,000 to 12,000 highly motivated and well-prepared soldiers who are executing offensive actions. According to the general, these soldiers operate using Soviet tactics, structured into platoons and companies, which enables them to execute coordinated and effective maneuvers. Their strength is largely derived from their numerical advantage, allowing them to rely on overwhelming force and unity in their operations. The strategy emphasizes the use of numbers to gain an upper hand in combat situations.
COURTESY: Kanal13
References
- ^ “Politics of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea”. Naenara. Retrieved 17 January 2025.
The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea is an independent socialist state guided by the great Kimilsungism–Kimjongilism in its activities.
- ^ “Korea, North”. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 6 December 2023. Archived from the original on 12 August 2015. Retrieved 8 December 2023.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Demographic Yearbook – Table 3: Population by sex, rate of population increase, surface area and density (PDF). United Nations Statistics Division. 2012. p. 5. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 August 2020. Retrieved 29 November 2014.
- ^ “North Korea country profile”. BBC News. 17 October 2023. Archived from the original on 7 June 2022. Retrieved 17 October 2023.
- ^ “Korea North”. The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 12 November 2024.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Real GDP (purchasing power parity)”. www.cia.gov. CIA World Factbook.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “GDP (PPP) per capita Field listing”. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 25 June 2014. Retrieved 31 May 2014.
- ^ “UNData app”. data.un.org. Archived from the original on 28 November 2022. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ “Decree on Redesignating Pyongyang Time”. Naenara. 30 April 2018. Archived from the original on 5 May 2018. Retrieved 4 May 2018.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Telephone System Field Listing”. CIA The World Factbook. Archived from the original on 25 June 2014. Retrieved 17 June 2014.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Hersher, Rebecca (21 September 2016). “North Korea Accidentally Reveals It Only Has 28 Websites”. NPR. Archived from the original on 22 September 2016. Retrieved 22 September 2016.
- ^ McCurry, Justin (16 January 2024). “Unification with South Korea no longer possible, says Kim Jong-un”. The Guardian. p. 1.
- ^ “Chapter I. Politics”. Socialist Constitution of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (2019) . 2019 – via Wikisource.
- ^ Korea原名Corea 美國改的名 (in Chinese). United Daily News. 5 July 2008. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 28 March 2014.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 72. ISBN 978-0-415-23749-9.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea’s Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 505–506. ISBN 978-0-393-32702-1.
- ^ Young, Benjamin R (7 February 2014). “Why is North Korea called the DPRK?”. NK News. Archived from the original on 9 February 2014. Retrieved 9 February 2014.
- ^ “Early Korea”. Archived from the original on 25 June 2015.
- ^ *매국사학의 몸통들아, 공개토론장으로 나와라!. ngonews. 24 December 2015. Archived from the original on 19 September 2016.
- 요서 vs 평양… 한무제가 세운 낙랑군 위치 놓고 열띤 토론. Segye Ilbo. 21 August 2016. Archived from the original on 13 April 2017.
- “갈석산 동쪽 요서도 고조선 땅” vs “고고학 증거와 불일치”. The Dong-a Ilbo. 22 August 2016. Archived from the original on 24 February 2021. Retrieved 14 April 2017.
- ^ Yi, Ki-baek (1984). A New History of Korea. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. pp. 12, 56. ISBN 978-0-674-61576-2.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea’s Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. p. 182. ISBN 978-0-393-32702-1.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea’s Place in the Sun: A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 174–175, 407. ISBN 978-0-393-32702-1.
- ^ Robinson, Michael E (2007). Korea’s Twentieth-Century Odyssey. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. pp. 84–86. ISBN 978-0-8248-3174-5.
- ^ Lone, Stewart; McCormack, Gavan (1993). Korea since 1850. Melbourne: Longman Cheshire. pp. 184–185.
- ^ Lone, Stewart; McCormack, Gavan (1993). Korea since 1850. Melbourne: Longman Cheshire. p. 175.
- ^ Robinson, Michael E (2007). Korea’s Twentieth-Century Odyssey. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. p. 113. ISBN 978-0-8248-3174-5.
- ^ Lankov, Andrei (16 March 2005). “North Korea’s missionary position”. Asia Times Online. Archived from the original on 18 March 2005. Retrieved 24 February 2024.
- ^ Robinson, Michael E (2007). Korea’s Twentieth-Century Odyssey. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. pp. 85–87, 155. ISBN 978-0-8248-3174-5.
- ^ “Administrative Population and Divisions Figures (#26)” (PDF). DPRK: The Land of the Morning Calm. Permanent Committee on Geographical Names for British Official Use. April 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 September 2006. Retrieved 10 October 2006.
- ^ Lankov, Andrei (25 January 2012). “Terenti Shtykov: the other ruler of nascent N. Korea”. The Korea Times. Archived from the original on 17 April 2015. Retrieved 14 April 2015.
- ^ Dowling, Timothy (2011). “Terentii Shtykov”. History and the Headlines. ABC-CLIO. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 26 April 2015.
- ^ Lankov, Andrei. “North Korea in 1945–48: The Soviet Occupation and the Birth of the State”. From Stalin to Kim Il Sung – The Formation of North Korea, 1945–1960. pp. 2–3.
- ^ Lankov, Andrei (10 April 2013). The Real North Korea: Life and Politics in the Failed Stalinist Utopia. Oxford University Press. p. 7.
- ^ “United Nations Security Council – History”. Encyclopedia Britannica. Archived from the original on 12 May 2021. Retrieved 12 May 2021.
- ^ “U.S.: N. Korea Boosting Guerrilla War Capabilities”. Fox News Network, LLC. Associated Press. 23 June 2009. Archived from the original on 27 June 2009. Retrieved 4 July 2009.
- ^ Kim, Samuel S. (2014). “The Evolving Asian System”. International Relations of Asia. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 45. ISBN 978-1442226418.
With three of the four major Cold War fault lines—divided Germany, divided Korea, divided China, and divided Vietnam – East Asia acquired the dubious distinction of having engendered the largest number of armed conflicts resulting in higher fatalities between 1945 and 1994 than any other region or sub-region. Even in Asia, while Central and South Asia produced a regional total of 2.8 million in human fatalities, East Asia’s regional total is 10.4 million including the Chinese Civil War (1 million), the Korean War (3 million), the Vietnam War (2 million), and the Pol Pot genocide in Cambodia (1 to 2 million).
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2011). The Korean War: A History. Modern Library. p. 35. ISBN 978-0812978964.
Various encyclopedias state that the countries involved in the three-year conflict suffered a total of more than 4 million casualties, of which at least 2 million were civilians—a higher percentage than in World War II or Vietnam. A total of 36,940 Americans lost their lives in the Korean theater; of these, 33,665 were killed in action, while 3,275 died there of nonhostile causes. Some 92,134 Americans were wounded in action, and decades later, 8,176 were still reported as missing. South Korea sustained 1,312,836 casualties, including 415,004 dead. Casualties among other UN allies totaled 16,532, including 3,094 dead. Estimated North Korean casualties numbered 2 million, including about one million civilians and 520,000 soldiers. An estimated 900,000 Chinese soldiers lost their lives in combat.
- ^ McGuire, James (2010). Wealth, Health, and Democracy in East Asia and Latin America. Cambridge University Press. p. 203. ISBN 978-1139486224.
In Korea, war in the early 1950s cost nearly 3 million lives, including nearly a million civilian dead in South Korea.
- ^ Painter, David S. (1999). The Cold War: An International History. Routledge. p. 30. ISBN 978-0415153164.
Before it ended, the Korean War cost over 3 million people their lives, including over 50,000 US servicemen and women and a much higher number of Chinese and Korean lives. The war also set in motion a number of changes that led to the militarization and intensification of the Cold War.
- ^ Lewy, Guenter (1980). America in Vietnam. Oxford University Press. pp. 450–453. ISBN 978-0199874231.
For the Korean War the only hard statistic is that of American military deaths, which included 33,629 battle deaths and 20,617 who died of other causes. The North Korean and Chinese Communists never published statistics of their casualties. The number of South Korean military deaths has been given as in excess of 400,000; the South Korean Ministry of Defense puts the number of killed and missing at 281,257. Estimates of communist troops killed are about one-half million. The total number of Korean civilians who died in the fighting, which left almost every major city in North and South Korea in ruins, has been estimated at between 2 and 3 million. This adds up to almost 1 million military deaths and a possible 2.5 million civilians who were killed or died as a result of this extremely destructive conflict. The proportion of civilians killed in the major wars of this century (and not only in the major ones) has thus risen steadily. It reached about 42 percent in World War II and may have gone as high as 70 percent in the Korean War. … we find that the ratio of civilian to military deaths [in Vietnam] is not substantially different from that of World War II and is well below that of the Korean War.
- ^ Armstrong 2010, p. 1: “The number of Korean dead, injured or missing by war’s end approached three million, ten percent of the overall population. The majority of those killed were in the North, which had half of the population of the South; although the DPRK does not have official figures, possibly twelve to fifteen percent of the population was killed in the war, a figure close to or surpassing the proportion of Soviet citizens killed in World War II.”
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (1997). Korea’s Place in the Sun: A Modern History. WW Norton & Company. pp. 297–298. ISBN 978-0-393-31681-0.
- ^ Jager 2013, pp. 237–242.
- ^ Stewart, Richard W., ed. (2005). “The Korean War, 1950–1953”. American Military History, Volume 2. United States Army Center of Military History. CMH Pub 30-22. Archived from the original on 28 May 2008. Retrieved 20 August 2007.
- ^ Abt 2014, pp. 125–126.
- ^ Brune, Lester H. (1996). The Korean War: Handbook of the Literature and Research. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 60. ISBN 978-0-313-28969-9.
- ^ “North Korea claims 1 million youth enlist amid drone tensions”. TRTWORLD. 16 October 2024. Retrieved 16 October 2024.
- ^ “North Korea says 1.4 million apply to join army amid tensions with South”. Reuters. 15 October 2024. Retrieved 16 October 2024.
- ^ Armstrong 2010, p. 9.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Chung, Chin O. Pyongyang Between Peking and Moscow: North Korea’s Involvement in the Sino-Soviet Dispute, 1958–1975. University of Alabama, 1978, p. 45.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Zagoria, Donald S.; Kim, Young Kun (December 1975). “North Korea and the Major Powers”. Asian Survey. 15 (12): 1017–1035. doi:10.2307/2643582. ISSN 0004-4687. JSTOR 2643582.
- ^ Country Study 2009, p. XV.
- ^ Schaefer, Bernd. “North Korean ‘Adventurism’ and China’s Long Shadow, 1966–1972”. Washington, D.C.: Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars, 2004.
- ^ Campbell, John Coert (196). American Policy Toward Communist Eastern Europe: The Choices Ahead. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. p. 116. ISBN 0-8166-0345-6.
- ^ Armstrong, Charles. Tyranny of the Weak: North Korea and the World, 1950–1992. Studies of the Weatherhead East Asian Institute, Columbia University. Cornell University Press. pp. 99–100.
- ^ Country Study 2009, pp. xxxii, 46.
- ^ French 2007, pp. 97–99.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2011). North Korea: Another Country. The New Press. p. 9. ISBN 978-1-59558-739-8.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Lankov, Andrei (2013). The Real North Korea: Life and Politics in the Failed Stalinist Utopia. OUP US. p. 64. ISBN 978-0-19-996429-1.
- ^ Demick, Barbara (16 July 2010). “North Korea’s giant leap backwards”. The Guardian. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- ^ Kirkbride, Wayne (1984). DMZ, a story of the Panmunjom axe murder. Hollym International Corp.
- ^ Bandow, Doug; Carpenter, Ted Galen, eds. (1992). The U.S.–South Korean Alliance: Time for a Change. New Brunswick: Transaction Publishers. pp. 99–100. ISBN 978-1-4128-4086-6. Archived from the original on 13 September 2016.
- ^ Chinoy, Mike (8 July 1997). “North Korea ends mourning for Kim Il Sung”. CNN. Archived from the original on 19 May 2015. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ^ Kwak, Tae-Hwan; Joo, Seung-Ho (2003). The Korean peace process and the four powers. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. ISBN 978-0-7546-3653-3.
- ^ DeRouen, Karl; Heo, Uk (2005). Defense and Security: A Compendium of National Armed Forces and Security Policies. ABC-CLIO.
- ^ “North Korea’s Military Strategy” Archived 24 February 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Parameters, U.S. Army War College Quarterly.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Spoorenberg, Thomas; Schwekendiek, Daniel (2012). “Demographic Changes in North Korea: 1993–2008”. Population and Development Review. 38 (1): 133–158. doi:10.1111/j.1728-4457.2012.00475.x. hdl:10.1111/j.1728-4457.2012.00475.x.
- ^ Jager 2013, p. 456.
- ^ Abt 2014, pp. 55, 109, 119.
- ^ Oberdorfer, Don; Carlin, Robert (2014). The Two Koreas: A Contemporary History. Basic Books. pp. 357–359. ISBN 978-0465031238.
- ^ Burns, Robert; Gearan, Anne (13 October 2006). “U.S.: Test Points to N. Korea Nuke Blast”. The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 5 October 2016. Retrieved 18 January 2020.
- ^ Bliss, Jeff (16 October 2006). “North Korea Nuclear Test Confirmed by U.S. Intelligence Agency”. Bloomberg News. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 16 October 2006.
- ^ Lee, Sung-Yoon (26 August 2010). “The Pyongyang Playbook”. Foreign Policy. Archived from the original on 4 September 2010. Retrieved 6 November 2010.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Anger at North Korea over sinking”. BBC News. 20 May 2010. Archived from the original on 23 May 2010. Retrieved 23 May 2010.
- ^ Deok-hyun Kim (24 November 2010). “S. Korea to toughen rules of engagement against N. Korean attack”. Archived from the original on 1 December 2010. Retrieved 24 November 2010.
- ^ Korean Central News Agency. “Lee Myung Bak Group Accused of Scuttling Dialogue and Humanitarian Work”. Archived from the original on 28 November 2010. Retrieved 24 November 2010.
- ^ “North Korean leader Kim Jong Il, 69, has died”. Associated Press. 19 December 2011. Archived from the original on 20 December 2011. Retrieved 19 December 2011.













