“Global Military Powers 2025: Nations Compete Fiercely to Boost Defence Budgets and Strengthen Military Might”

Global Military Powers 2025: The Rise of Geopolitical Tensions and Escalating Conflicts
The world in 2025 is witnessing an unparalleled level of insecurity, with an escalating number of armed conflicts across various regions. According to recent reports, approximately 60 active conflicts were documented in the past year—the highest number ever recorded. This surge in violence is reshaping the global landscape, pushing military preparedness to the forefront of international concerns.
Surge in Civilian Fatalities
The human cost of these conflicts has been devastating. As per the World Economic Forum, civilian fatalities have increased by more than 30% from 2023 to 2024, with the most significant toll being observed in the Middle East, North Africa, and Eastern Europe. The brutal escalation of hostilities, particularly in regions like Ukraine, Syria, and Libya, has exacerbated humanitarian crises, displacing millions and intensifying suffering among non-combatant populations.
Geopolitical Strife and Regional Instability
The ongoing conflict in Ukraine and the deepening crisis in the Middle East have drawn global attention. The growing instability in these regions has far-reaching implications, not only for national security but for international alliances and power structures. Nations are increasingly forced to rethink their foreign policies and military strategies, while tensions between major powers, such as the U.S., China, and Russia, continue to rise.
In North Africa, armed groups have capitalized on political vacuums, further destabilizing fragile governments and contributing to the proliferation of violent extremism. Eastern Europe, particularly the Balkans, also remains a flashpoint as tensions flare between NATO allies and Russia.
The Role of Military Power in Global Stability
As the world grapples with these conflicts, military capabilities have become more crucial than ever. Countries are pouring vast resources into modernizing their forces, enhancing defense technologies, and building stronger military alliances. Nations are aware that military power is not only a tool for protecting borders but also for asserting influence in a rapidly changing global order.
The ongoing arms race has led to the formation of strategic defense pacts, with countries vying to secure their positions on the world stage. In particular, nations in the Asia-Pacific and Europe are fortifying their defenses in response to growing threats from regional adversaries. The military balance in these areas will be decisive in shaping future global dynamics.
Warfare as the Foremost Threat to Global Stability
The 2025 Global Risks Report highlights warfare as the foremost threat to global stability. With international diplomacy struggling to manage escalating tensions, military intervention and defense strategies have become critical in maintaining peace and security. As conflicts continue to intensify, the need for global cooperation and conflict resolution mechanisms becomes more pressing.
The rise in armed conflicts and the surge in military investments are symptoms of a broader trend where countries, driven by fear of insecurity, are turning to military power as a means to safeguard their sovereignty. The shift towards a more militarized world presents both challenges and opportunities for the international community, requiring careful diplomacy and innovative solutions to prevent further escalation.
In conclusion, the global military powers in 2025 are navigating a complex landscape marked by fierce geopolitical competition, unprecedented conflict rates, and shifting power dynamics. The future of international security depends on how effectively nations balance military preparedness with diplomatic efforts to address the root causes of conflict.
Soaring Military Expenditures: A $2.4 Trillion Surge in Global Defense Spending
In stark contrast to the rising global insecurity, military expenditures have reached unprecedented heights. According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), global military spending hit an astounding $2.4 trillion in 2023, marking a dramatic increase in defense budgets across nations. This surge in military expenditures underscores the intensifying global competition for military dominance and the growing priority placed on national defense in a time of heightened geopolitical instability.
Rising Military Budgets Amidst Global Tensions
Countries are increasingly allocating vast sums to bolster their military capabilities, driven by escalating conflicts and perceived threats. Nations are modernizing their armed forces, investing in advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, cybersecurity defense systems, and next-generation weaponry. The growing concern over territorial security, arms races, and power struggles in key regions like Eastern Europe, the Asia-Pacific, and the Middle East has catalyzed this spending spree.
The Largest Military Budgets: Leading Global Powers
The United States remains the world’s largest spender on military affairs, with a defense budget surpassing $800 billion in 2023. China follows closely behind, with its defense spending continuing to rise as part of its broader strategy to assert itself as a global military powerhouse. Other significant contributors include Russia, India, and European nations, each investing heavily to maintain and enhance their military readiness.
The Implications of Soaring Defense Budgets
This surge in global military spending has significant implications for global stability. While it signals preparedness and strength, it also raises concerns about the potential for an arms race, particularly in regions where tensions are already high. The concentration of vast resources in military development diverts funds from critical sectors such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure, potentially exacerbating socio-economic inequalities and instability.
Moreover, the growing trend of militarization highlights the shift in global power dynamics, with countries prioritizing defense capabilities over diplomatic solutions. This shift further complicates efforts to foster international cooperation, leaving global peace increasingly fragile.
The Road Ahead: Balancing Military Power and Diplomacy
As military spending continues to climb, it is crucial for the international community to strike a balance between enhancing defense capabilities and promoting diplomatic dialogue. A reliance on military power as a primary tool for national security poses risks of conflict escalation, and finding peaceful resolutions to disputes remains a critical challenge for global governance. In the face of mounting military expenditures, the need for effective conflict resolution mechanisms, arms control agreements, and multilateral cooperation has never been more urgent.
The Race for Military Power: Nations Prioritize Defense over Global Stability
As countries strive to assert themselves as dominant global players, the competition to enhance military capabilities has reached unprecedented levels. Nations are channeling vast financial resources into defense and military initiatives, reflecting their economic ambitions and strategic goals. This military buildup is not just a response to immediate security threats but also a calculated effort to project power, influence international relations, and shape the global political landscape.
Military Strength as a Strategic Imperative
In an increasingly multipolar world, nations view military strength as a cornerstone of their global standing. A robust military not only deters adversaries but also enables countries to exert influence over key geopolitical issues. For major powers, military capabilities are intertwined with economic ambitions—defense budgets are seen as a reflection of a nation’s status and capacity to shape international policies. As a result, military investments are skyrocketing, with countries eager to modernize their armed forces, develop cutting-edge technologies, and enhance their global strategic presence.
Economic Ambitions and Global Influence
The race for military supremacy is a strategic maneuver aimed at gaining a competitive edge in global politics. Nations with advanced military assets are better positioned to participate in international decision-making, safeguard trade routes, and engage in peacekeeping or peace-enforcing missions. Military power, in this sense, becomes an indispensable tool in shaping global narratives, securing economic interests, and maintaining regional dominance. Countries that lag behind in defense capabilities risk being marginalized in international diplomacy and conflict resolution.
A Grim Outlook for Global Peace
While the emphasis on military power strengthens the position of individual nations, it casts a shadow over global peace and stability. The growing arms race has diverted attention and resources away from pressing global challenges such as poverty, climate change, and public health. The imperative for peaceful conflict resolution is increasingly overshadowed by the pursuit of military dominance, further complicating efforts to foster international cooperation.
The pursuit of military strength, rather than promoting peace, is intensifying geopolitical tensions, with rivalries heightening and arms races spiraling in key regions. The risk of miscalculations or accidental escalations grows as nations focus on enhancing their defensive and offensive capabilities. The world is at a tipping point, where military might is prioritized over diplomacy, pushing global stability into a precarious position.
Conclusion: The Need for Balance
In this high-stakes environment, the pursuit of military superiority may offer short-term strategic gains but risks undermining long-term global stability. The challenge moving forward is finding a balance between military preparedness and the collective pursuit of peace. Nations must recognize that true global influence comes not only from military power but also from diplomacy, cooperation, and the ability to address the root causes of conflict. Without a concerted effort to prioritize peace alongside defense, the world risks continuing down a path of escalating militarization and instability.
Global Firepower Index 2025: Top 10 most powerful countries in the world by military
The Global Firepower Military Strength Ranking for 2025 has just been released, evaluating the military strengths of 145 countries around the globe. This comprehensive ranking is based on over 60 individual factors, each contributing to the overall Power Index score. These factors include defense budgets, manpower, technological capabilities, logistical strength, natural resources, and strategic positioning. The ranking offers a detailed snapshot of the world’s most powerful militaries, highlighting the countries that dominate in terms of military readiness, capabilities, and global influence.
Key Factors in the Power Index:
- Defense Budgets: The financial resources allocated to defense and military developments, which determine a country’s ability to fund modern equipment, maintain forces, and sustain long-term military readiness.
- Personnel: The size and training level of a country’s armed forces, including active-duty personnel and reserves.
- Weapons and Equipment: The type, quantity, and technological sophistication of a country’s weaponry, including ground forces, air force, naval capabilities, and missile systems.
- Logistics and Infrastructure: A nation’s ability to deploy and sustain military operations globally, including transportation, supply lines, and communication infrastructure.
- Geopolitical Position: The strategic importance of a country’s location, which influences its defense priorities, alliances, and vulnerability to external threats.
- Nuclear Capabilities: The possession of nuclear weapons and the strategic role these play in deterrence, global positioning, and defense doctrine.
The Top 10 Global Military Powers (2025):
Based on the latest Global Firepower Military Strength Ranking, here are the top 10 most powerful militaries:
- United States
- China
- Russia
- India
- Japan
- France
- United Kingdom
- South Korea
- Turkey
- Germany
Each of these nations brings a unique combination of resources, technology, and strategic military doctrines, allowing them to project power on a global scale and influence international security dynamics.
Conclusion:
The Global Firepower Ranking provides a vital assessment of global military capabilities, emphasizing the growing importance of technological advancements and strategic positioning in defining military power. As nations continue to invest heavily in defense, the global landscape remains competitive, with countries constantly seeking to enhance their military readiness for both regional and global challenges.
Unsurprisingly, the United States of America has reaffirmed its position as the unrivaled leader in military strength in the Global Firepower Military Strength Ranking 2025. This position has been maintained since 2005, a testament to the U.S.’s unmatched military capabilities, which include:
- Extensive Manpower: A large, highly trained, and well-equipped military force, with millions of active-duty personnel and reserves.
- Financial Resources: The U.S. defense budget, which consistently surpasses $800 billion, enables investment in cutting-edge technologies, advanced weapons systems, and global military deployments.
- Material Reserves: The U.S. maintains substantial reserves of military hardware, including aircraft, tanks, naval vessels, and ammunition, ensuring its operational readiness.
- Industrial Output: The United States has a robust defense industry that can rapidly produce state-of-the-art military equipment and maintain its global military presence.
These elements collectively ensure the United States remains a dominant global military power, with the ability to influence geopolitical outcomes and defend its interests worldwide.
Russia: The Powerhouse in the East
In the second position, Russia has solidified its military strength despite the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict. Its Power Index score of 0.0788 reflects a potent military force bolstered by key advantages:
- Nuclear Arsenal: Russia’s formidable nuclear capabilities continue to be a cornerstone of its military strategy and global deterrence.
- Ground Forces: Russia maintains one of the largest standing armies in the world, with significant mechanized infantry, artillery, and tanks.
- Strategic Alliances: Despite international sanctions and the Russia-Ukraine war, Russia’s alliances with countries like China, North Korea, and Iran enhance its military positioning. These partnerships provide not only economic and military support but also strategic leverage in global politics.
- Technological Advancements: Russia is increasingly investing in advanced defense technologies, including hypersonic weapons, anti-satellite systems, and cutting-edge missile defense systems.
These factors have helped Russia maintain its position as the second most powerful military in the world, positioning it as a critical player in global security and geopolitics.
Conclusion:
The United States continues to dominate the global military landscape, with its superior resources, technological innovation, and military reach. However, Russia remains a formidable force, leveraging alliances and strategic positioning to assert its power. As geopolitical tensions continue to rise, these two military giants are poised to shape global security dynamics well into the future.
In third place, China closely trails Russia with a Power Index score of 0.0788, highlighting its growing military might and strategic significance. China’s rise as a global military power is underscored by several key factors:
1. Strategic Alliance with Russia:
- China’s alliance with Russia enhances its geopolitical influence and military capabilities. This partnership strengthens both countries’ positions on the world stage, particularly in areas such as defense technology and energy resources. Their mutual interests, especially in countering U.S. influence, continue to shape their military strategies and security cooperation.
2. Expanding Military Capabilities:
- China has made substantial investments in modernizing its military, especially its navy, air force, and missile systems. Its military budget has consistently risen, allowing for the procurement of advanced weaponry, including stealth fighters, ballistic missiles, and naval assets.
- The People’s Liberation Army (PLA) has rapidly expanded its capabilities, focusing on cyber warfare, space technology, and anti-satellite weapons, aiming to create a multi-dimensional military force.
3. Robust Industrial Base:
- China’s military-industrial complex plays a crucial role in its military strength. The country’s manufacturing capacity allows for the production of a vast array of military equipment, including state-of-the-art fighter jets, ships, tanks, and surveillance systems.
- This self-sufficiency in defense production ensures that China can sustain and grow its military power without reliance on external sources.
4. Regional Influence and Global Reach:
- Asia: China has strategically enhanced its military presence in the South China Sea, where it continues to assert territorial claims, and along its borders, particularly with India and Russia. Its nuclear capabilities and military installations across the region serve to solidify its influence.
- Africa and South America: China’s growing diplomatic and economic ties with nations in Africa and South America have been complemented by expanding military cooperation, including arms sales, joint training, and peacekeeping missions, further enhancing its global influence.
- Belt and Road Initiative (BRI): Through the BRI, China has expanded its political and economic influence across continents, strengthening its global military partnerships and gaining strategic footholds in key regions.
5. Technological Advancements:
- China’s continued push for technological innovation has seen the development of cutting-edge military technologies, such as hypersonic weapons, AI-powered defense systems, and quantum communication systems. These advancements are rapidly positioning China as a technological leader in the military sector.
Conclusion:
China’s growing military capabilities, fueled by substantial defense investments and a robust industrial base, have firmly positioned it as the third most powerful military force in the world. Its alliance with Russia, strategic military expansion, and increasing influence across Asia, Africa, and South America further strengthen its global power projection. As China continues to enhance its military prowess, it will remain a dominant player in shaping global security and geopolitical dynamics.
The military landscape in 2025 features several notable players whose rising defense capabilities reflect both economic growth and strategic alignments. These countries, driven by increasing defense budgets, expanding industrial sectors, and strategic military partnerships, are asserting themselves as key players on the global stage. Among them:
1. South Korea – 5th Position
- South Korea has solidified its position as the 5th most powerful military globally. Its Power Index score continues to improve thanks to:
- Cutting-edge technological advancements in areas like missile defense and cyber warfare.
- A strong alliance with the United States, particularly in the realm of defense technologies and military training, which enhances its strategic deterrence, especially against the threat from North Korea.
- Significant investments in naval power and air defense systems, including advanced fighter jets and naval vessels.
2. Japan – 7th Position
- Japan has advanced into the 7th position with a highly capable self-defense force that boasts:
- Technological superiority in naval and air power, particularly in submarine technology and advanced missile defense systems.
- Strategic alliances, particularly with the United States, allowing Japan to access advanced military technologies and integrate closely with NATO forces.
- Defensive posture focused on regional security concerns, particularly in the East China Sea and Pacific Ocean, where it seeks to balance China’s rising influence.
3. Türkiye – 8th Position
- Turkey ranks 8th, driven by a robust and expanding military capacity, supported by:
- A rapidly developing defense industry, which produces advanced systems such as drones, rockets, and tanks, making Turkey a regional power with a growing global presence.
- Strategic alliances within NATO, allowing for access to advanced military technologies, while also developing independent military capabilities.
- Turkey’s geopolitical position in the Middle East and its role in addressing regional conflicts, including those in Syria and Libya, has strengthened its military relevance.
4. Iran – 14th Position
- Iran, ranking 14th, continues to be a key military force in the Middle East due to:
- Strong regional influence, with a significant military presence in countries like Syria, Iraq, and Lebanon.
- Increasing investments in missile technologies, including ballistic and cruise missiles, which allow it to project power across the region.
- Strong alliances with Russia and China, which provide both strategic support and military technology transfers.
- Despite facing sanctions, Iran’s military self-sufficiency in various sectors, including drones and missile technology, has allowed it to maintain a strong military presence.
Key Factors Behind Their Military Growth:
- Rising Defense Budgets: These countries have significantly increased their military budgets to modernize their forces, develop advanced technologies, and expand their strategic capabilities.
- Thriving Industrial Sectors: The growth of domestic defense industries in these nations has enabled them to reduce dependence on foreign military suppliers, while also driving innovation in key areas such as drones, missiles, and advanced aircraft.
- Strategic Partnerships: All these nations have benefited from strategic military partnerships with global powers:
- South Korea and Japan maintain close ties with the United States, gaining access to advanced military technologies.
- Turkey balances its NATO membership with increasing independence in defense development, creating a blend of Western and indigenous military strength.
- Iran, while facing international sanctions, leverages its alliances with Russia and China to enhance its military capabilities.
Conclusion:
Countries like South Korea, Japan, Turkey, and Iran represent rising military powers that are enhancing their global military standing through investments in defense, advanced technologies, and strategic partnerships. While these nations have different geopolitical and defense priorities, they are all positioned to play critical roles in regional and global security dynamics in the years ahead.
Here is a table of the Top 10 Most Powerful Militaries in the World as of 2025:
| Rank | Country | Power Index Score | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States | 0.0711 | Largest defense budget, cutting-edge technology, global reach. |
| 2 | Russia | 0.0788 | Strong nuclear arsenal, military alliances, vast manpower. |
| 3 | China | 0.0788 | Expanding military power, strategic alliances, advanced tech. |
| 4 | India | 0.0962 | Large manpower, nuclear capabilities, strategic positioning. |
| 5 | South Korea | 0.1367 | Technological advancements, strong U.S. alliance, regional defense. |
| 6 | France | 0.1433 | Advanced air and naval forces, nuclear deterrence. |
| 7 | Japan | 0.1551 | Technological superiority, strategic alliances, strong defense posture. |
| 8 | Turkey | 0.1789 | Growing defense industry, regional power, NATO member. |
| 9 | Germany | 0.1896 | High-tech military capabilities, NATO member, strong economy. |
| 10 | United Kingdom | 0.2015 | Strong naval power, nuclear weapons, strategic alliances. |
This table reflects the rankings based on Global Firepower’s Power Index for 2025, which evaluates military strength based on over 60 factors, including manpower, technological advancements, defense spending, and geopolitical alliances.
Where do India and Pakistan stand on the Global Firepower Index 2025?
As of 2025, India and Pakistan are ranked as follows on the Global Firepower Index:
- India: Ranked 4th globally with a Power Index score of 0.0962. India has a large military workforce, nuclear capabilities, and is strategically positioned in South Asia, contributing to its strong standing in the global military ranking.
- Pakistan: Ranked 13th globally with a Power Index score of 0.2896. Pakistan, while having significant nuclear capabilities and strong conventional forces, is ranked lower than India due to factors such as a smaller defense budget and fewer technological advancements.
This reflects India’s higher military strength and technological capabilities compared to Pakistan, though both countries are significant regional military powers in South Asia.
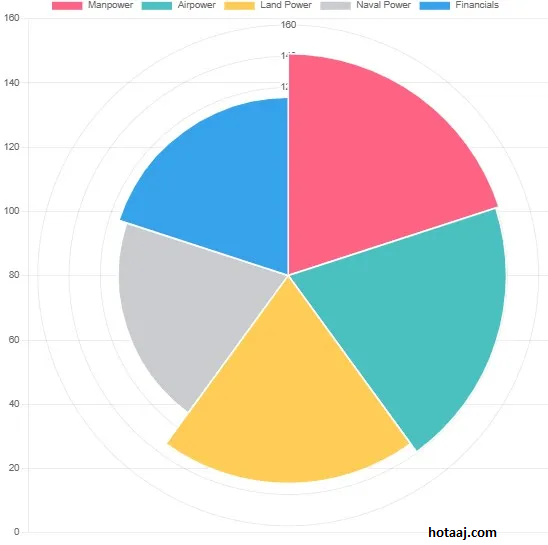
As of 2025, here’s a more detailed breakdown of the military rankings for India and Pakistan on the Global Firepower Index:
India – Ranked 4th
- Power Index Score: 0.0962
- Key Strengths:
- Manpower: India maintains one of the largest standing armies in the world, which bolsters its military power.
- Nuclear Capabilities: India is a nuclear-armed state with strategic deterrence in place.
- Technological Advancements: Significant investments in defense technology, such as advanced air defense systems, missiles, and combat aircraft.
- Naval and Air Forces: India has a strong naval fleet, including aircraft carriers, and modern fighter jets. Its Air Force is one of the largest in Asia.
- Defense Spending: India consistently increases its military budget, which allows modernization and the acquisition of cutting-edge technology.
- Strategic Positioning: India’s geopolitical position in South Asia and its alliances with global powers such as the United States and Russia further enhance its military standing.
Pakistan – Ranked 13th
- Power Index Score: 0.2896
- Key Strengths:
- Nuclear Capabilities: Pakistan is also a nuclear-armed state, with a strong strategic deterrence against regional threats.
- Manpower: Pakistan has a large and well-trained military, though not as expansive as India’s, it remains formidable.
- Conventional Forces: The Pakistan Army is highly focused on defense and offense capabilities, especially in terms of artillery and special operations forces.
- Air Force and Naval Power: Pakistan has made strides in developing modern fighter jets, submarines, and missile systems.
- Defense Budget: While Pakistan’s defense budget is lower than India’s, the country focuses on prioritizing defense in its budget allocations.
- Strategic Alliances: Pakistan benefits from its strong military partnership with China, which provides access to defense technologies and trade. Additionally, Pakistan has support from other regional powers.
Comparative Analysis (India vs. Pakistan):
- Global Ranking: India is positioned significantly higher than Pakistan, reflecting its stronger defense budget, technological advancements, and a more diversified military portfolio.
- Nuclear Deterrence: Both nations possess nuclear weapons, but India’s nuclear deterrence is seen as more robust due to its advanced delivery systems (missiles, submarines, etc.) and larger arsenal.
- Technological Edge: India continues to advance in military technologies, with significant investments in air defense systems, space-based military tech, and aircraft. Pakistan is growing its defense capabilities but faces technological gaps in comparison.
- Regional Power: While both nations exert considerable influence in South Asia, India’s larger military, economic power, and strategic alliances provide it with a more dominant regional and global role.
In summary, India’s position in the Top 5 reflects its growing military power, advanced technology, and global alliances, while Pakistan, though a significant military player, lags behind India due to fewer resources and technological advancements, placing it at 13th in the rankings.
Courtesy: leo chart
References
- ^ Jump up to:a b Khan, Yasmin (2007). The great Partition: the making of India and Pakistan. Yale University Press. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-300-12078-3. Retrieved 30 October 2011.
- ^ * Ambedkar, Bhimrao Ramji (1945) [first published as Thoughts on Pakistan, 1940], Pakistan or Partition of India, Bombay: Thacker and company, p. 5
- ^ Dixit, Jyotindra Nath (2002). India-Pakistan in War & Peace. Routledge. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-415-30472-6.
- ^ P. 4“Cause for acceptance of refugees into European Nations” (PDF). Dhruv Kharabanda. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 April 2017. Retrieved 9 October 2019.
- ^ Population of independent Pakistan (East + West) was 60 million. Population of Muslims in Indian dominion was 30 million or 9% of total population.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Talbot & Singh 2009, p. 2.
- ^ Population Redistribution and Development in South Asia. Springer Science & Business Media. 2012. p. 6. ISBN 978-9400953093. Archived from the original on 16 January 2023. Retrieved 9 October 2019.
- ^ “Instrument of Accession”, White Paper on Indian States (1950)/Part 4/Instrument of Accession, Wikisource, archived from the original on 8 March 2021, retrieved 9 October 2019
- ^ Prasad, S.N.; Dharm Pal (1987). History of Operations in Jammu and Kashmir 1947–1948. New Delhi: History Department, Ministry of Defence, Government of India. (printed at Thomson Press (India) Limited). p. 418.
- ^ Hagerty, Devin (2005). South Asia in World Politics. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 161. ISBN 9780742525870. Archived from the original on 6 February 2023. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
- ^ The Kingfisher History Encyclopedia. Kingfisher. 2004. p. 460. ISBN 9780753457849. Archived from the original on 6 February 2023. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
- ^ New Zealand Defence Quarterly, Issues 24-29. New Zealand. Ministry of Defence. 1999. Archived from the original on 6 February 2023. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
- ^ Thomas, Raju (1992). Perspectives on Kashmir: the roots of conflict in South Asia. Westview Press. p. 25. ISBN 9780813383439. Archived from the original on 6 February 2023. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
- ^ David R. Higgins 2016.
- ^ Rachna Bisht 2015.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d Lyon, Peter (2008). Conflict between India and Pakistan: an encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. p. 82. ISBN 978-1-57607-712-2. Archived from the original on 7 February 2023. Retrieved 30 October 2011.
- ^ Dijink, Gertjan (2002). National Identity and Geopolitical Visions: Maps of Pride and Pain. Routledge. ISBN 9781134771295.
The superior Indian forces, however, won a decisive victory and the army could have even marched on into Pakistani territory had external pressure not forced both combatants to cease their war efforts.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Pakistan :: The Indo-Pakistani War of 1965”. Library of Congress Country Studies, United States of America. April 1994. Archived from the original on 7 January 2016. Retrieved 2 October 2010. Quote: Losses were relatively heavy–on the Pakistani side, twenty aircraft, 200 tanks, and 3,800 troops. Pakistan’s army had been able to withstand Indian pressure, but a continuation of the fighting would only have led to further losses and ultimate defeat for Pakistan.
- ^ Hagerty, Devin (2005). South Asia in world politics. Rowman & Littlefield, 2005. p. 26. ISBN 0-7425-2587-2. Archived from the original on 5 February 2023. Retrieved 15 November 2015. Quote: The invading Indian forces outfought their Pakistani counterparts and halted their attack on the outskirts of Lahore, Pakistan’s second-largest city. By the time United Nations intervened on 22 September, Pakistan had suffered a clear defeat.
- ^ Wolpert, Stanley (2005). India (3rd ed. with a new preface. ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press. p. 235. ISBN 0520246969. Archived from the original on 30 March 2023. Retrieved 15 November 2015. Quote: India, however, was in a position to inflict grave damage to, if not capture, Pakistan’s capital of the Punjab when the cease-fire was called, and controlled Kashmir’s strategic Uri-Poonch bulge, much to Ayub’s chagrin.
- ^ Till, Geoffrey (2004). Seapower: a guide for the twenty-first century. Great Britain: Frank Cass Publishers. p. 179. ISBN 0-7146-8436-8. Retrieved 28 May 2010.
- ^ Christophe Jaffrelot, Gillian Beaumont (28 September 2004). A History of Pakistan and Its Origins. Anthem Press, 2004. ISBN 1-84331-149-6.
- ^ Times Staff and Wire Reports (30 March 2002). “Gen. Tikka Khan, 87; ‘Butcher of Bengal’ Led Pakistani Army”. Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 19 June 2021. Retrieved 30 October 2011.
- ^ Ahsan, Syed Badrul (15 July 2011). “A Lamp Glows for Indira Gandhi”. The Daily Star. Archived from the original on 24 February 2021. Retrieved 30 October 2011.
- ^ Nawaz, Shuja (2008). Crossed Swords: Pakistan, Its Army, and the Wars Within. Oxford University Press. p. 329. ISBN 978-0-19-547697-2.
- ^ Chitkara, M. G (1996). Benazir, a Profile – M. G. Chitkara. APH. p. 81. ISBN 9788170247524.
- ^ Schofield, Victoria (2003). Kashmir in Conflict: India, Pakistan and the Unending War – Victoria Schofield. Bloomsbury Academic. p. 117. ISBN 978-1-86064-898-4.
- ^ Leonard, Thomas (2006). Encyclopedia of the developing world. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-415-97662-6.
- ^ “BBC NEWS | India Pakistan | Timeline”. news.bbc.co.uk. Archived from the original on 11 October 2017. Retrieved 22 April 2022.
- ^ Ali, Tariq (1997). Can Pakistan Survive? The Death of a State. Verso Books. ISBN 0-86091-949-8. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 26 October 2020.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c Wolpert, Stanley (14 August 2010). “Recent Attempts to Resolve the Conflict”. India and Pakistan: Continued Conflict or Cooperation?. University of California Press. pp. 73. ISBN 9780520271401.
- ^ Ali, Tariq. “Bitter Chill of Winter”. London Review of Books=. Archived from the original on 1 October 2009. Retrieved 20 May 2009.
- ^ Colonel Ravi Nanda (1999). Kargil: A Wake Up Call. Vedams Books. ISBN 81-7095-074-0. Online summary of the Book Archived 28 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Kargil: where defence met diplomacy Archived 16 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine – India’s then Chief of Army Staff VP Malik, expressing his views on Operation Vijay. Hosted on Daily Times; The Fate of Kashmir By Vikas Kapur and Vipin Narang Archived 18 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine Stanford Journal of International Relations; Book review of “The Indian Army: A Brief History by Maj Gen Ian Cardozo” Archived 8 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine – Hosted on IPCS
- ^ Jump up to:a b R. Dettman, Paul (2001). “Kargil War Operations”. India Changes Course: Golden Jubilee to Millennium. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 119–120. ISBN 9780275973087.
- ^ Samina Ahmed. “Diplomatic Fiasco: Pakistan’s Failure on the Diplomatic Front Nullifies its Gains on the Battlefield” Archived 4 August 2011 at the Wayback Machine (Belfer Center for International Affairs, Harvard Kennedy School)
- ^ Daryl Lindsey and Alicia Montgomery. “Coup d’itat: Pakistan gets a new sheriff”. salon.com. Archived from the original on 20 December 2009. Retrieved 19 June 2015.
- ^ “War in Kargil – The CCC’s summary on the war” (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 February 2004. Retrieved 20 May 2009.
- ^ Samina Ahmed. “A Friend for all Seasons.” Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine (Belfer Center for International Affairs, Harvard Kennedy School)
- ^ “Rediff on the NeT: Pakistan refuses to take even officers’ bodies”. rediff.com. Archived from the original on 24 February 2021. Retrieved 19 June 2015.
- ^ “press release issued in New Delhi regarding bodies of two Pakistan Army Officers” Archived 15 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Second-Class Citizens by M. Ilyas Khan, The Herald (Pakistan), July 2000. Online scanned version of the article Archived 21 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Musharraf and the truth about Kargil[usurped] – The Hindu 25 September 2006
- ^ “Over 4000 soldier’s killed in Kargil: Sharif”. The Hindu. Archived from the original on 11 November 2012. Retrieved 20 May 2009.
- ^ Kapur, S. Paul (2007). Dangerous Deterrent: Nuclear Weapons Proliferation and Conflict in South Asia (23rd ed.). Stanford University Press. p. 227. ISBN 978-0804755498.
- ^ MacDonald, Myra (2017). Defeat is an Orphan: How Pakistan Lost the Great South Asian War. Oxford University Press. pp. 27, 53, 64, 66. ISBN 978-1-84904-858-3.
p. 27: It was not so much that India won the Great South Asian War but that Pakistan lost it.p. 53: The story of the Kargil War—Pakistan’s biggest defeat by India since 1971 —is one that goes to the heart of why it lost the Great South Asian War.p. 64: Afterwards, Musharraf and his supporters would claim that Pakistan won the war militarily and lost it diplomatically. In reality, the military and diplomatic tides turned against Pakistan in tandem.p. 66: For all its bravado, Pakistan had failed to secure even one inch of land.Less than a year after declaring itself a nuclear-armed power, Pakistan had been humiliated diplomatically and militarily.
- ^ Lavoy, Peter René, ed. (2009). Asymmetric Warfare in South Asia: The Causes and Consequences of the Kargil Conflict. Cambridge University Press. p. 180. ISBN 978-0-521-76721-7.
The false optimism of the architects of the Kargil intrusion, colored by the illusion of a cheap victory, was not only the main driver of the operation, and hence the crisis, it also was the cause of Pakistan’s most damaging military defeat since the loss of East Pakistan in December 1971.
- ^ Wirsing, Robert (15 February 1998). India, Pakistan, and the Kashmir dispute: on regional conflict and its resolution. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 77. ISBN 978-0-312-17562-7. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ “India’s renewed strategy of destabilising Balochistan”. Daily Times. 20 August 2018. Archived from the original on 1 February 2019. Retrieved 31 January 2019.
- ^ “Indian campaigning on Balochistan continues”. www.thenews.com.pk. Archived from the original on 1 February 2019. Retrieved 31 January 2019.
- ^ Roy, Rajesh (September 2021). “Taliban Takeover Threatens to Raise India-Pakistan Tensions”. Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on 14 December 2021. Retrieved 14 December 2021.
- ^ “India-Pakistan Rivalry in Afghanistan”. 25 March 2010. Archived from the original on 14 December 2021. Retrieved 14 December 2021.
- ^ “Coalition Vows to Regain Afghan Town Seized by Taliban”. The New York Times. 18 July 2006. Archived from the original on 20 December 2019. Retrieved 14 December 2021.
- ^ “India-Pakistan tug-of-war jeopardizes Afghan peace process | Asia | An in-depth look at news from across the continent”. Deutsche Welle. 18 May 2020. Archived from the original on 18 December 2020. Retrieved 17 February 2022.
- ^ Malik, Saleem Akhtar (7 August 2017). “Remember the hero of Lakshmipur: Major Tufail!”. Global Village Space. Retrieved 2 June 2024.
- ^ Weisman, Steven R. (6 March 1987). “On India’s border, a huge mock war”. The New York Times. Archived from the original on 30 January 2011. Retrieved 30 October 2011.
- ^ “Musharraf declares war on extremism”. South Asia. BBC. 12 January 2002. Archived from the original on 25 February 2022. Retrieved 30 October 2011.
- ^ Freeze, Colin (11 April 2011). “Accused in India massacre claims ties to Pakistani secret service – The Globe and Mail”. The Globe and Mail. Toronto. Archived from the original on 15 September 2018. Retrieved 1 September 2017.
- ^ “Rana, Headley implicate Pak, ISI in Mumbai attack during ISI chief’s visit to US”. The Times of India. 12 April 2011. Archived from the original on 11 August 2011.
- ^ “Diplomat denies Pakistan role in Mumbai attacks”. The Independent. London. 31 January 2009. Archived from the original on 19 July 2018. Retrieved 1 September 2017.
- ^ Khan, Zarar (1 December 2008). “Pakistan Denies Government Involvement in Mumbai Attacks”. Huffington Post. Archived from the original on 18 May 2014. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- ^ King, Laura (7 January 2009). “Pakistan denies official involvement in Mumbai attacks”. Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 26 February 2017. Retrieved 11 December 2019.
- ^ “Indian jets violating Pakistani airspace ‘technical incursion’, says Zardari (Fourth Lead) – Thaindian News”. Thaindian.com. 14 December 2008. Archived from the original on 9 July 2014. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- ^ “Pak might soon move troops from border with India”. The Times of India. 16 June 2009. Archived from the original on 11 August 2011.
- ^ “India’s surgical strikes across LoC: Full statement by DGMO Lt Gen Ranbir Singh”. Hindustan Times. 29 September 2016. Archived from the original on 2 October 2016. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ^ Perry, Juliet. “Pakistan captures Indian soldier in Kashmir”. cnn.com. Archived from the original on 1 October 2016.
- ^ Miglani, Sanjeev; Hashim, Asad (29 September 2016). “India says hits Pakistan-based militants, escalating tensions”. Reuters. Archived from the original on 5 October 2016. Retrieved 5 October 2016.
- ^ Abbas, Syed Sammer (29 September 2016). “Army rubbishes Indian ‘surgical strikes’ claim as two Pakistani soldiers killed at LoC”. Dawn. Archived from the original on 30 September 2016. Retrieved 30 September 2016.
- ^ Masood, Salman (1 October 2016). “In Kashmir, Pakistan Questions India’s ‘Surgical Strikes’ on Militants”. The New York Times. Archived from the original on 5 October 2016. Retrieved 1 October 2016.
- ^ Haider, Abrar (29 September 2016). “Pakistan captures one Indian soldier, eight killed at LoC overnight”. Dawn. Archived from the original on 30 September 2016. Retrieved 29 September 2016.
- ^ “Indian soldiers killed in clashes with Pakistan Army”. The News. 29 September 2016. Archived from the original on 30 September 2016. Retrieved 30 September 2016.
- ^ “Indian Army Says Soldier in Pak Custody Was Not Captured During Surgical Strikes”. NDTV.com. 30 September 2016. Archived from the original on 30 September 2016. Retrieved 30 September 2016.
- ^ “India evacuates 10,000 from border with Pakistan amid reprisal fears after Kashmir ‘strikes'”. Daily Telegraph. 30 September 2016. Archived from the original on 1 October 2016. Retrieved 30 September 2016.
- ^ “So-called surgical strike: Indian farce throws up a few challenges”. Express Tribune. 1 October 2016. Archived from the original on 2 October 2016. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ^ “Pulwama terror attack today: 40 CRPF jawans martyred in IED blast in Jammu and Kashmir’s Pulwama | India News – Times of India”. The Times of India. 16 February 2019. Archived from the original on 15 February 2019. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ “India Hits Main Jaish Camp in Balakot, “Non-Military” Strike: Government”. NDTV. Archived from the original on 27 February 2019. Retrieved 26 February 2019.
- ^ “Pakistan army confirms Indian jets dropped ‘four bombs'”. The Times of India. Press Trust of India. Archived from the original on 26 February 2019. Retrieved 28 February 2019.
- ^ “Statement by Foreign Secretary on 26 February 2019 on the Strike on JeM training camp at Balakot”. mea.gov.in. Archived from the original on 27 February 2019. Retrieved 21 March 2019.
- ^ “Viewpoint: India strikes in Pakistan a major escalation”. 26 February 2019. Archived from the original on 13 May 2019. Retrieved 26 February 2019.
- ^ Fisk, Robert (28 February 2019). “Israel is playing a big role in India’s escalating conflict with Pakistan”. The Independent. Archived from the original on 1 October 2019. Retrieved 12 October 2019.
- ^ Peer, Basharat (2 March 2019). “Opinion | The Young Suicide Bomber Who Brought India and Pakistan to the Brink of War”. The New York Times. Archived from the original on 3 February 2021. Retrieved 21 March 2019.
- ^ Abi-Habib, Maria; Ramzy, Austin (25 February 2019). “Indian Jets Strike in Pakistan in Revenge for Kashmir Attack”. The New York Times. Archived from the original on 27 February 2019. Retrieved 21 March 2019.
- ^ Gettleman, Jeffrey; Kumar, Hari; Yasir, Sameer (2 March 2019). “Deadly Shelling Erupts in Kashmir Between India and Pakistan After Pilot Is Freed”. The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2 March 2019. Retrieved 21 March 2019.
- ^ Gurung, Shaurya Karanbir (29 March 2019). “A month after Indian air strike, Pakistan takes journalists to Balakot site”. The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 4 June 2021. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- ^ “Foreign journalists given access to madressah near site of Balakot strike”. DAWN.COM. 10 April 2019. Archived from the original on 25 July 2021. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- ^ “43 Days After Balakot Air Strike by IAF, Pakistan Takes Media Team And Diplomats to ‘Site'”. News18. 10 April 2019. Archived from the original on 4 June 2021. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- ^ “2 Indian aircraft violating Pakistani airspace shot down; pilot captured”. DAWN.COM. 27 February 2019. Archived from the original on 27 February 2019. Retrieved 21 March 2019.
- ^ Khan, M. Ilyas (1 March 2019). “Fighter pilot ‘opened fire’ before capture”. BBC News. Archived from the original on 1 March 2019. Retrieved 21 March 2019.
- ^ Iain Marlow and Kamran Haider (27 February 2019). “Pakistan Downs Two Indian Jets, Pilot Arrested, Army Says”. Bloomberg.com. Archived from the original on 4 April 2019. Retrieved 27 February 2019.
- ^ “ISPR releases ‘proof’ further contradicting Indian claim of shooting down F-16”. DAWN.COM. 5 April 2019. Archived from the original on 13 September 2019. Retrieved 4 October 2019.
- ^ “India, Pakistan came close to firing missiles at each other on February 27”. Hindustan Times. 23 March 2019. Retrieved 9 October 2019.
- ^ Seligman, Lara (4 April 2019). “Did India Shoot Down a Pakistani Jet? U.S. Count Says No”. Archived from the original on 23 November 2021. Retrieved 4 October 2019.
- ^ “‘Not aware’: Pentagon on Pak F-16 count after Feb aerial dogfight with IAF”. Hindustan Times. 6 April 2019. Retrieved 9 October 2019.
- ^ Lalwani, Sameer; Tallo, Emily. “Analysis | Did India shoot down a Pakistani F-16 in February? This just became a big deal”. Washington Post. Archived from the original on 30 November 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ “Pakistan radio transmissions showed F-16 didn’t return to its base: IAF”. The Economic Times. 6 April 2019. Archived from the original on 24 April 2019. Retrieved 9 October 2019.
- ^ “Indian Radar Data That Supposedly Proves They Downed An F-16 Is Far From “Irrefutable””. The Drive. 8 April 2019. Archived from the original on 17 April 2019. Retrieved 9 October 2019.
- ^ “Repetitions don’t turn lies into truth: DG ISPR on IAF presser”. Express Tribune. 8 April 2019. Archived from the original on 8 February 2021. Retrieved 30 January 2021.
- ^ Achom, Debanish (9 October 2019). “On Air Force Day, IAF Disproves Pak Claim Of Shooting Down Sukhoi Fighter”. NDTV. Archived from the original on 29 March 2021. Retrieved 29 March 2021.
- ^ “India, Pakistan report deadly violence along Kashmir border”. Al Jazeera English. 13 November 2020. Archived from the original on 24 January 2021. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- ^ “India, Pakistan report deadly violence along Kashmir border”. Al Jazeera. 13 November 2020. Archived from the original on 24 January 2021. Retrieved 11 March 2022.
- ^ “India, Pakistan militaries agree to stop cross-border firing in rare joint statement”. Reuters. 25 February 2021. Archived from the original on 11 March 2022. Retrieved 11 March 2022.
- ^ “Joint Statement”. pib.gov.in. Archived from the original on 10 April 2022. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- ^ “Inter Services Public Relations Pakistan”. ispr.gov.pk. Archived from the original on 20 May 2022. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- ^ Pakistani plane “may have crossed border” Archived 18 October 2002 at the Wayback Machine 13 August 1999 BBC Retrieved 23 July 2007
- ^ “The Case concerning the Aerial Incident of 10th August, 1999 – Summaries of Judgments and Orders”. International Court of Justice. 21 June 2000. Archived from the original on 15 October 2016. Retrieved 18 December 2011.
- ^ “In 2011 five security men were martyred, according to the Indian Sources”. IBN Live. Archived from the original on 9 January 2015.
- ^ “Kashmir border deaths spark India and Pakistan row”. BBC. 1 September 2011. Archived from the original on 5 December 2018. Retrieved 2 September 2011.
- ^ “LoC: Three Pakistani soldiers died in attack by Indian forces”. The Express Tribune. 1 September 2011. Archived from the original on 14 December 2011. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- ^ “Pak troops kill two jawans, behead, mutilate one of them”. The Times of India. Archived from the original on 19 January 2013.
- ^ “India and Pakistan exchange fire along border in Kashmir”. UPI. Archived from the original on 10 June 2020. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ Xia, Lili; Robock, Alan; Scherrer, Kim; Harrison, Cheryl S.; Bodirsky, Benjamin Leon; Weindl, Isabelle; Jägermeyr, Jonas; Bardeen, Charles G.; Toon, Owen B.; Heneghan, Ryan (15 August 2022). “Global food insecurity and famine from reduced crop, marine fishery and livestock production due to climate disruption from nuclear war soot injection”. Nature Food. 3 (8): 586–596. doi:10.1038/s43016-022-00573-0. hdl:11250/3039288. ISSN 2662-1355. PMID 37118594. S2CID 251601831.
- ^ “India-Pakistan nuclear war could kill 2 billion people: Study”. WION. 16 August 2022. Archived from the original on 17 November 2022. Retrieved 17 November 2022.
- ^ “India’s Nuclear Weapons Program – Smiling Buddha: 1974”. nuclearweaponarchive.org. Retrieved 22 April 2022.
- ^ “Fact Sheet — Nov 5, 2019: Pakistan Nuclear Overview”. The Nuclear Threat Initiative (NTI). Nuclear Threat Initiative. 5 November 2019. Archived from the original on 7 September 2022. Retrieved 23 August 2022.
- ^ Khan, Munir Ahmad (18 May 1974). “India’s nuclear explosion: Challenge and Response”. International Atomic Energy Agency and Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission. JSTOR 3096318. Retrieved 22 April 2022.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Koh Kambaran (Ras Koh Hills)”. Pakistan Paedia. Archived from the original on 30 November 2011. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- ^ “Pakistan’s Nuclear Weapons Program – Development”. nuclearweaponarchive.org. Retrieved 22 April 2022.
- ^ “Rediff on the NeT: It was ‘Operation Shakti’ on Budh Purnima”. Rediff.com. 16 May 1998. Archived from the original on 2 May 2013. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- ^ Herald Exclusive By Pervez Hoodbhoy 16 February 2011 (16 February 2011). “Herald exclusive: Pakistan’s nuclear bayonet | Pakistan”. Dawn.Com. Archived from the original on 18 February 2011. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- ^ “28 May 1998 – Pakistan nuclear tests: CTBTO Preparatory Commission”. www.ctbto.org. Archived from the original on 7 July 2017. Retrieved 22 April 2022.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Pakistan’s Nuclear Weapons Program – 1998: The Year of Testing”. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- ^ Baloch, Shah Meer. “The Fallout From Pakistan’s Nuclear Tests”. thediplomat.com. Archived from the original on 20 March 2022. Retrieved 22 April 2022.













